Incoherent X-ray diffraction calculations¶
Overview of Usage¶
Here is a description probably with examples ccchange
Module Listing¶
- class IncoherentXray.IncoherentXrayScattering(D=1, L=1, axis='z', symmetry='scc')¶
- ListPlanes_Cubic(latticeConstant, k)¶
- According to the apparatus geometry, make a list of avaible reflection planes.
- ReciprocalPrimitiveVectors_CubicLattice(latticeConstant=1, strain=None)¶
- Calculate the reciprocal primitive vectors for simple cubic lattice in the presence of elastic strain.
- RetrieveSpatialInformation(hkl, region, rodrigues, strain=None, scale=None, k0=12, beamwidth=0.01, systemshape=None, screenlatticesize=128)¶
Return a boolean array of the size hkl.shape which corresponds to the real space information that in turn corresponds to a certain region of the diffraction pattern.
Region in terms of screen coordinates in the form of a boolean array of size (screenlatticesize, screenlatticesize)
Rodriques is the typical rodrigues vector provided to the other x-ray functions.
- RodriguesToSpots(rodrigues, strain=None, scale=None, k0=7, beamwidth=0.10000000000000001)¶
This function turns rodrigues vector field into X-ray diffraction spots. Notice that 1) Strain scales the same as the rodrigues vector. 2) Everything is based on small deformation approximation.
We assume the simple cubic lattice here.
- Returns tuple of 3 arrays containing as indices
- 0: x screen position of a spot
- 1: y screen position of a spot
- 2: intensity of the spot at the given x,y position
- SimulateXrayDiffractionImage(rodrigues, strain=None, scale=None, k0=12, beamwidth=0.01, hkl=None, screenlatticesize=128)¶
Perform the entire Incoherent X-ray simulation given a set of rodrigues vectors and produce the real-space image of the diffraction on the experimental screen.
- Required parameters:
- rodrigues: a 3 vector of rotation values
- Options available:
- strain: strain values for the same rodriques rotation values
- k0: center of the beam’s x-ray wavevector
- beamwidth: spread of the beam as
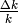
- hkl: a set of lattice vectors to use. If Null then use all.
- VectorRotatingUnderRodriguesVector(vector, rodrigues, scale=None)¶
- The direction of Rodrigues vector defines the rotation axis; the magnitude of Rodrigues vector defines the rotation angle.