
DEFINITIONS OF SI UNITS
|
Search
A, C, F,
H, J, K,
L, M, N,
O, R, S,
V, W |
|
A
ampere (A)
The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight
parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross section,
and placed 1 meter apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors
a force equal to 2*10-7 newton per meter of
length.
C
candela (cd)
The candela is the luminous intensity, in the perpendicular direction,
of a surface of 1/600000 square meter of a blackbody at the temperature of
freezing platinum under a pressure of 101325 newtons per square meter.
coulomb (C)
The coulomb is the quantity of electricity transported in 1 second
by a current of 1 ampere.
F
farad (F)
The farad is the capacitance of a capacitor between the plates of
which there appears a difference of potential of 1 volt when it is charged
by a quantity of electricity equal to 1 coulomb.
H
henry (H)
The henry is the inductance of a closed circuit in which an electromotive
force of 1 volt is produced when the electric current in the circuit varies
uniformly at a rate of 1 ampere per second.
J
joule (J)
The joule is the work done when the point of application of I newton
is displaced a distance of 1 meter in the direction of the force.
K
kelvin (K)
The kelvin, unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273.16
of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
kilogram (kg)
The kilogram is the unit of mass; it is equal to the mass of the
international prototype of the kilogram. (The international prototype of
the kilogram is a particular cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy which is
preserved in a vault at Sevres, France, by the International Bureau of Weights
and Measures.)
L
lumen (lm)
The lumen is the luminous flux emitted in a solid angle of 1 steradian
by a uniform point source having an intensity of 1 candela.
M
meter (m)
The meter is the length equal to 1650763.73 wavelengths in vacuum
of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the levels
2p10 and 5d5 of the krypton-86 atom.
mole (mol)
The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as
many elementary entities as there are carbon atoms in 0.012kg of carbon 12.
The elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions,
electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles.
N
newton (N)
The newton is that force which gives to a mass of 1 kilogram an
acceleration of 1 meter per second per second.
O
ohm ( 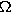 )
)
The ohm is the electric resistance between two points of a conductor
when a constant difference of potential of 1 volt, applied between these
two points, produces in this conductor a current of 1 ampere, this conductor
not being the source of any electromotive force.
R
radian (rad)
The radian is the plane angle between two radii of a circle which
cut off on the circumference an arc equal in length to the radius.
S
second (s)
The second is the duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation
corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground
state of the cesium-133 atom.
steradian (sr)
The steradian is the solid angle which, having its vertex in the center
of a sphere, cuts off an area of the surface of the sphere equal to that
of a square with sides of length equal to the radius of the sphere.
V
volt (V)
The volt is the difference of electric potential between two points
of a conducting wire carrying a constant current of 1 ampere, when the power
dissipated between these points is equal to 1 watt.
W
watt (W)
The watt is the power which gives rise to the production of energy
at the rate of 1 joule per second.
weber (Wb)
The weber is the magnetic flux which, linking a circuit of one turn,
produces in it an electromotive force of 1 volt as it is reduced to zero
at a uniform rate in 1 second.

