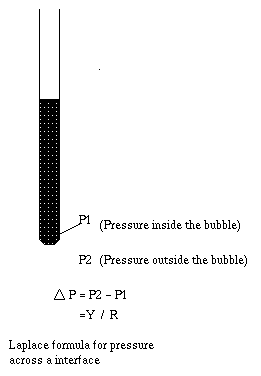
- decreasing the interfacial tension ( Y )
- increasing the radius of the capillary pore (R).
This can be understood as: surfactants reduce (interfacial
tension): Cosine(contact angle) ~1/(interfacial tension), therefore as Cosine(contact angle) increases the contact angle decreases.