Contents
TopThe Paper
Problems for Further Study
The Program
The Source Code
More on Hysteresis
The Windows Interface
Running the Simulation
![]() To start the simulation
switch to the directory containing the file HysteresisSimulation.exe
and double click on the icon shown on the left to run the
HysteresisSimulation Program. If you wish to output data
from the simulation, make sure that the subdirectories "data"
and "data\average" exist for the program to write to.
To start the simulation
switch to the directory containing the file HysteresisSimulation.exe
and double click on the icon shown on the left to run the
HysteresisSimulation Program. If you wish to output data
from the simulation, make sure that the subdirectories "data"
and "data\average" exist for the program to write to.
Starting your first run
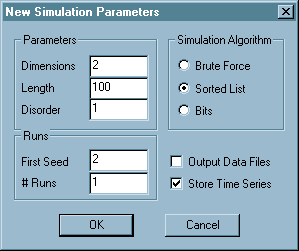
When the simulation starts, the first thing you see will be a "New Simulation Parameters" dialog box like the one shown to the right. The above dialog box contains parameters for using the sorted list algorithm to run a single 2-dimensional 100x100 simulation with Rc=1.0 and a starting random number seed of 2. Because the "Store Time Series" box is checked, the simulation will record the entire time series of the simulation. The size of the time series scales with the size of the simulation, so if you are running low on memory you may want to uncheck this box. If you check the "Output Data Files" box, the simulation will output data for each run of the simulation, and output average data after all runs are complete. If this box is unchecked, you will still have the opportunity to output average data when all of the runs are complete. Change the "First Seed" to run the simulation with a different set of random fields. Change the "# runs" to get data averaged over a number of instantiations of the random fields.
The User Interface
Once your first simulation has started, you will get a new window which contains various views of the simulation results. These views will be described in more detail in the next section, The Views. Initially, only the lattice view will be visible. At the top of the screen you will see the control bar shown above. You will use this control bar to control the program. In the rest of this section, we will describe in detail each of the buttons on the control bar.
| Create a new simulation. This will bring up the "New Simulation Parameters" dialog box described above. | |
| View the average correlation function for the completed runs. | |
| View the average avalanche size distribution for the completed runs. | |
| View the M(H) curve for the current run. | |
| View the time series for the current run. | |
| Save the average correlation function and avalanche size distribution. | |
| Save a snapshot of the lattice to disk. | |
| Make a printout of the current view. | |
| Get help on the HysteresisSimulation program. |
The Views
This section describes the various views of the data which are available. For more information about the functions which are plotted, see our paper.The Lattice View
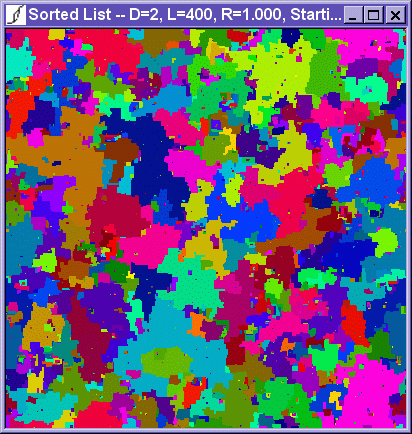
The lattice view is a picture of the lattice. Unflipped spins are colored black, and each avalanche of flipped spins is colored a different color. In dimensions higher than two, all avalanches are projected into two dimensions and avalanches will overlap eachother.
The Correlation Function View
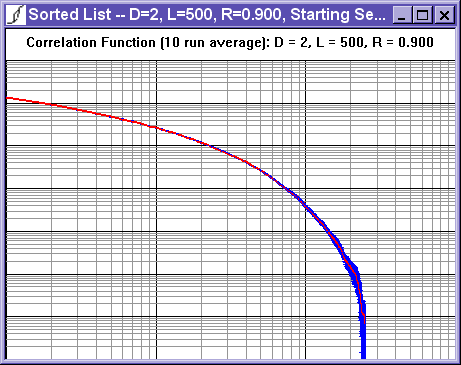
The correlation function view displays the average correlation function for all runs completed so far. It is plotted on a log-log plot, where each large line represents a multiple of ten. The blue error bars show the standard deviation from run to run.
The Avalanche Size Distribution View
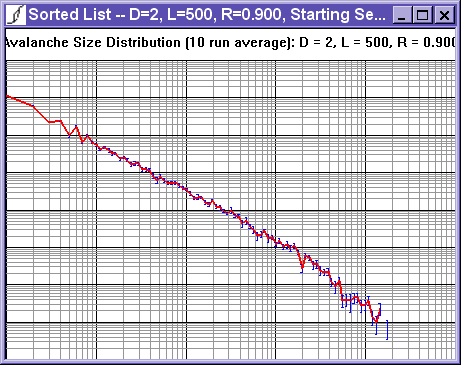
The avalanche size distribution view shows the average avalanche size distribution on a log-log plot. The blue error bars represent the standard deviation from run to run.
The M(H) View
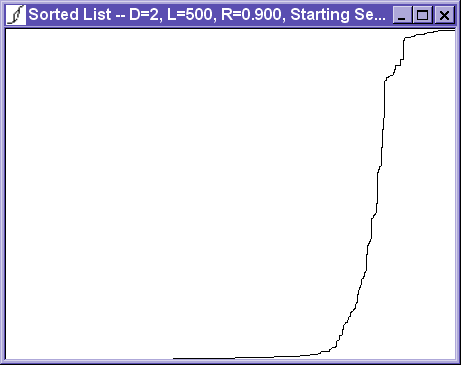
The M(H) View shows the magnetization as a function of time. The magnetization, M, is shown on the vertical axis, with M=1 at the top, and M=-1 at the bottom. The magnetic field, H, is shown on the horizontal axis.
The Time Series View
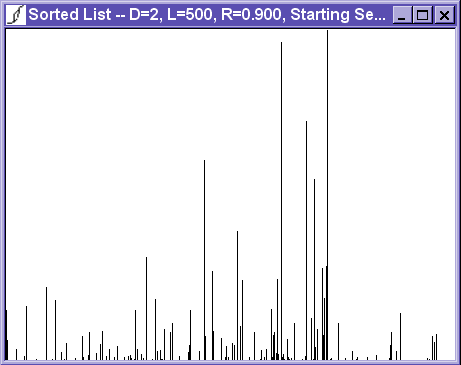
The time series view shows the avalanche sizes as a function of time. With the assumption that the magnetic field, H, is being increased at a constant rate. (Therefore, it is also a graph of avalanche size as a function of H.)