 |
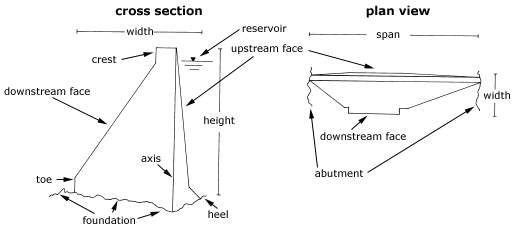
What are the parts
of a gravity dam? |
|
abutment (*)
axis (*)
crest (*)
cross section (*)
downstream face (*)
|
foundation (*)
heel (*)
height (*)
plan view (*)
reservoir (*)
|
span (*)
toe (*)
upstream face (*)
width (*)
|
Gravity dams use their weight to hold back the water in the reservoir.
Gravity dams can be made of earth or rock fill or concrete. In this section
we will concentrate on concrete gravity dams. These dams can be very
expensive because of how much material they use.
Generally, the base of a concrete gravity dam is equal to approximately 0.7
times the height of the dam:
base = 0.7 * height
crest = 0.2 * height
The shape of the gravity dam resembles a triangle. This is because of the
triangular distribution of the water pressure. The deeper the water, the more
horizontal pressure it exerts on the dam. So at the surface of the reservoir,
the water is exerting no pressure and at the bottom of the reservoir, the
water is exerting maximum pressure. The shape can vary slightly; any of these
shapes can be used for a simulation of a gravity dam if the exact shape is not
known. |
|
Roll over each shape of gravity dam:
plain
vertical top
slanted upstream face
|
 |
|
The slant on the upstream face in the third shape allows water to weigh down
on the dam, increasing its stability.
|
How would you model a
gravity dam for a simulation?
You would model a cross-section of the gravity dam, like the
cross-section shown above. A cross-section is a two-dimensional slice through the
dam, showing the width and the height of the dam.
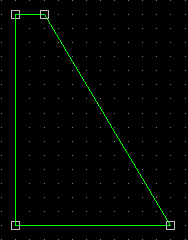
To the right, a model of a gravity dam with an
inspection passageway is shown.
Your model should be scaled down from the real dam; that is, the size of
you model of the dam should be a proportion of the size of the actual
dam. |
|
 |
How is the dam attached to the ground?
Probably just like your house, the dam is sitting on a foundation.
The foundation should be solid rock for a concrete gravity dam. The dam
should not be able to move; we call this fixed. In a
simulation, you must tell the program that your dam is "fixed" at the bottom
and that it can't move up, down, left, right, front, or back. In a
2-dimensional simulation, you should fix the foundation in both the x and
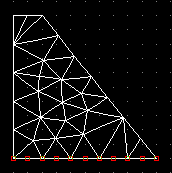
y directions. Here is an example of a model which has been fixed at the
foundation -- see the red dots along the bottom? The engineer told
the program that the dam is fixed along the bottom edge. |
  |


