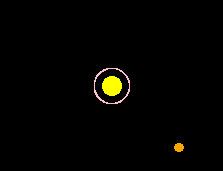
Jupiter, Earth, and Sun
After Newton's triumph in explaining Kepler's laws, the
next natural question was how the mutual gravitational forces between the
planets affected their motion. Vast efforts were spent understanding
how the exact solution to the two-body problem was possible: the key
role of integrals of the motion (energy, momentum, angular momentum, and
one special to the inverse square law) was recognized, and a vast effort
to identify integrals in the three-body problem was launched. This ended
with a proof that there were not enough analytic integrals of the motion,
and (more recently) with the demonstration that there are initial conditions
where the motion is chaotic.
The lack of an exact solution led to some insecurity. Simple
calculations of the strength of Jupiter's force on Earth suggested that,
unless exceptional cancellation occurred, the Earth's orbit should be
significantly perturbed on historical time scales.
Questions
Q: If the force of Jupiter on the Earth were applied constantly
in the direction of the Earth's motion, how long would it take for the
Earth to reach escape velocity and leave the Solar System?
Can you check this with the simulation? Try shifting "View" to
"Earth's Trajectory" to speed things up. You can zoom with the
right mouse button to see the small effects of Jupiter on Earth.
Jupiter:
How to Get Jupiter
Jupiter is available
for Windows 95, Windows NT, Macintosh, and several Unix platforms
(the IBM RS6000, Sun Sparc, Dec Alpha (courtesy Kamal Bhattacharya),
Linux, and the PowerPC running AIX4.1).
The files are available without charge by anonymous FTP
(ftp.lassp.cornell.edu) or
via
the World Wide Web.
Last modified: May 19, 1996
James P. Sethna,
sethna@lassp.cornell.edu.
 Statistical Mechanics: Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity,
now available at
Oxford University Press
(USA,
Europe).
Statistical Mechanics: Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity,
now available at
Oxford University Press
(USA,
Europe).





![]() Statistical Mechanics: Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity,
now available at
Oxford University Press
(USA,
Europe).
Statistical Mechanics: Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity,
now available at
Oxford University Press
(USA,
Europe).